- 8 Marks
ICMA – Nov 2024 – L1 – Q2b – Working Capital
Calculates total amount held in working capital excluding cash and equivalents.
Question
Working Capital Calculation
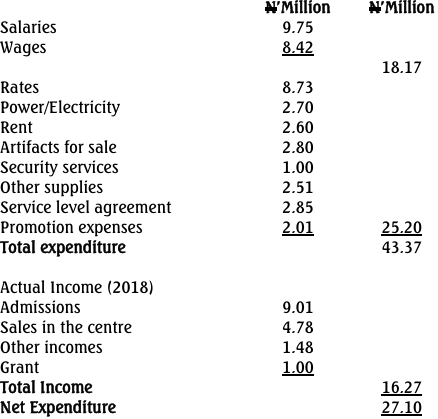
A company has annual sales revenues of GH¢45 million and the following working capital periods:
| Working Capital Item | Period (months) |
|---|---|
| Inventory conversion period | 2.5 |
| Accounts receivable collection period | 2.0 |
| Accounts payable payment period | 1.5 |
Production costs are 70% of sales revenue.
Required:
Calculate the total amount held in working capital excluding cash and cash equivalents.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Budgeting, Costing, Inventory
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Budgeting, Cost and Cost Behaviour
- Series: Nov 2024
Report an error