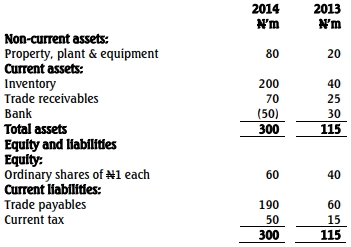
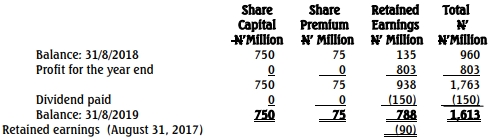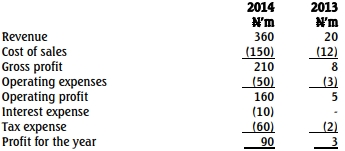- 5 Marks
FR – Nov 2024 – L2 – Q5d – Revenue Recognition under IFRS 15
Analyzing distinct performance obligations in a software contract under IFRS 15.
Question
Togbah LTD (Togbah), a software developer, enters into a contract with a customer to transfer the following:
- Software licence
- Installation service (includes changing the web screen for each user)
- Software updates
- Technical support for two years
Togbah sells the above separately. The installation service is routinely performed by other entities and does not significantly modify the software. The software remains functional without the updates and the technical support.
Required:
Explain whether the goods or services promised to the customer are distinct in terms of IFRS 15: Revenue from Contracts with Customers
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Report an error