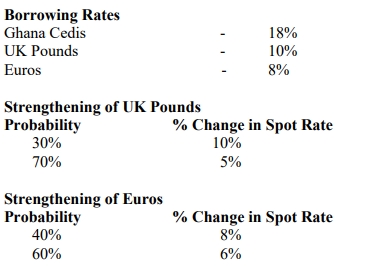
- 20 Marks
FR – May 2018 – L2 – Q4 – Consolidated Financial Statements (IFRS 10)
Assess the financial performance and position of two companies using specified ratios and explain the limitations of ratio analysis.
Question
Ibadan Nigeria Limited is considering acquiring a suitable private limited liability company. The board of directors engaged a financial consultant to analyze the financial position of two companies, Abuja Limited and Rivers Limited, which are both receptive to the acquisition. The draft financial statements of the two companies are as follows:
Statements of Profit or Loss
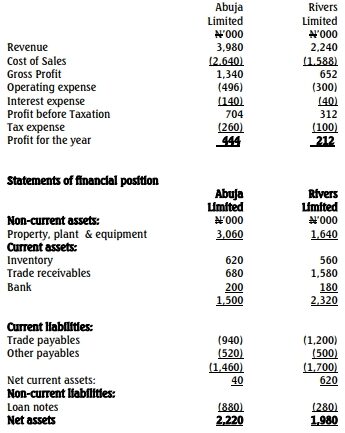

a. Draft a report to the chairman of the board of directors of Ibadan Limited to assess the financial performance and position of the two companies using the following specific ratios: (12 Marks) i. Profitability ratios: Gross profit percentage and net profit margin. ii. Liquidity ratios: Acid test ratio, current ratio, trade receivable period. iii. Long-term financial stability ratios: Gearing ratio and proprietary ratio. iv. Efficiency ratios: Total asset turnover and non-current asset turnover.
b. Explain the limitations of ratio analysis and further information that may be useful to the board of directors when making the acquisition decision. (8 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.