Beposo Ltd is an agro-processing company, whose head office is in the Greater Accra region of Ghana. The trial balance of the company for the year ended 31 December 2021 is as follows:
Additional Information:
i) Included in the revenue figure is sales made on special arrangement, payable by customers in two years’ time at an amount of GH¢16.8 million. The cash price of the sales at the date of the sales (i.e. 1 January 2021) is estimated at GH¢15 million, and the effective interest rate of the arrangement has been computed as 5.83% per annum.
ii) Non-current assets consist of the following classes of assets: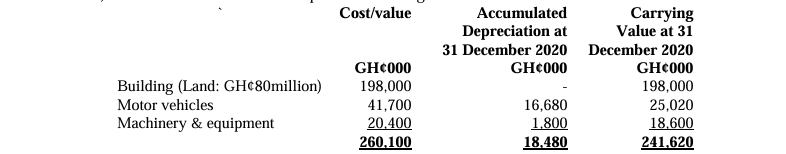
The company revalues its buildings periodically to ensure that the carrying value reflects their fair market value. On 31 December 2020, the buildings were revalued at GH¢198 million, of which GH¢80 million was attributed to land. The revaluation surplus shown in the trial balance represents the increase in value recorded during this revaluation. All buildings were completed and ready for use on 1 January 2011. The company’s buildings serve as administrative offices and production centers, and they have an estimated useful life of 50 years.
In 2021, the company relocated from one of its administrative offices and sold the building on 1 April 2021 for GH¢27.6 million. The revalued amount and revaluation surplus for this building as of 31 December 2020 were GH¢25 million (with GH¢5 million for the land) and GH¢8 million, respectively. On 31 December 2021, the remaining land and buildings were revalued at GH¢169.35 million, with GH¢85 million attributed to the land. The company’s policy is to recognize revaluation surplus only upon derecognition of the non-current asset.
The sale of the building and the 2021 revaluation of the remaining buildings have not yet been recorded in the company’s books. The payment for the sale of the building was received in the first week of January 2022. There were no other changes to the value of property, plant, and equipment during the year ended 31 December 2021.
Depreciation for 2021 has not been accounted for in the trial balance. The company charges depreciation to cost of sales. Motor vehicles, machinery, and equipment are depreciated over five years.
In lieu of a cash dividend, the company issued bonus shares on 1 January 2021 at a ratio of one new share for every ten existing shares, priced at GH¢1 per share. The issuance was subject to an 8% withholding tax, which has already been paid by the company and is included in administrative expenses. The bonus shares, which are in respect of the year ended 31 December 2020, have not yet been recorded.
After 31 December 2021, the Board of Directors proposed a dividend of GH¢0.80 per share in respect of the year ended 31 December 2021. The dividend has not yet been approved by shareholders.
The provision for tax in the trial balance reflects the under or over provision of tax for the year ended 31 December 2020, based on the difference between the tax estimated for the year and the actual liability determined after a tax audit. The current tax liability for 2021 is estimated at GH¢16.7 million. Taxable temporary differences as at 31 December 2021, arising from discrepancies between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases, amount to GH¢60 million. The applicable corporation tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Prepare the following financial statements for Beposo Ltd for the year ended 31 December 2021:
i) Statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income
ii) Statement of changes in equity
iii) Statement of financial position as at that date.
(Total: 20 marks)


