- 30 Marks
Question
Gbenga Alimi wants to establish a fast food restaurant in Koko, a state in Naijaland. A well-known global fast-food outfit in Naijaland has agreed to give him a franchise to operate the business in the state. However, the franchisor has requested Gbenga to present a viable business plan for assessment.
Required:
a. Outline the contents of a business plan addressing the proposed franchise’s viability. (20 Marks)
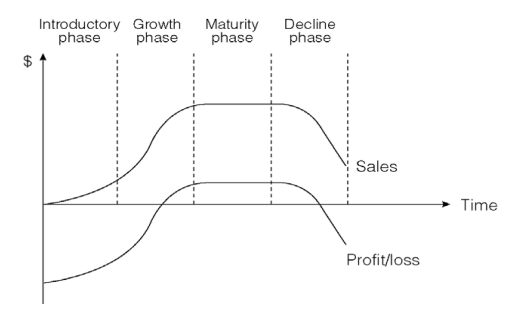
b. Use a graphical representation to educate Gbenga on the four stages of the classical product life cycle. (6 Marks)
c. Within an organizational context, distinguish between:
i. Narrow and wide stakeholders
ii. Active and passive stakeholders
(4 Marks)
Answer
- a. Components of a Business Plan:
- Title page: Attracts readers and assists them in finding the report later, usually includes the title, author, organization’s name, reference numbers, confidentiality degree, date, and relevant artwork such as a logo.
- Table of contents: Lists all sections with page numbers.
- Introduction: Prepares readers, explaining the subject, purpose, and methods.
- Executive Summary: Summarizes key points for busy readers.
- Business Description: Details the business, its history, products, and unique factors.
- Market Analysis: Identifies target market, demand, trends, competitors, and pricing.
- Marketing Plan: Outlines promotion, distribution, and pricing strategies.
- Operations Plan: Describes daily business processes, location, facilities, and equipment.
- Management Plan: Details management team, organizational structure, and staffing.
- Financial Plan: Projects revenue, expenses, profitability, and funding needs
- b. Product Life Cycle Stages:
- Introduction: Product is launched, with low sales and high investment.
- Growth: Sales increase, brand recognition improves, and profit margins grow.
- Maturity: Sales peak, market saturation occurs, and competition is high.
- Decline: Sales decline due to new innovations or changing consumer preferences.
The stages should be represented in a standard product life cycle graph
- c. Stakeholder Analysis:
- Narrow vs. Wide Stakeholders:
- Narrow stakeholders: Directly impacted, such as shareholders and employees.
- Wide stakeholders: Less directly impacted, including government and wider community.
- Active vs. Passive Stakeholders:
- Active stakeholders: Involved in decision-making, like employees and managers.
- Passive stakeholders: Not directly involved, but interested, e.g., local communities and government
- Narrow vs. Wide Stakeholders:
- Tags: Business Plan, Franchise, Product Life Cycle, Stakeholders, Strategic Planning, Viability
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Strategic Planning Process
- Series: MAY 2017
- Uploader: Theophilus
