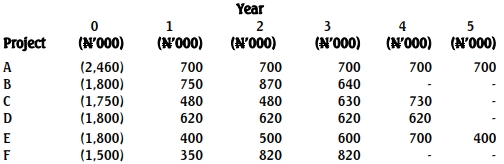
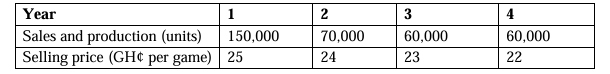
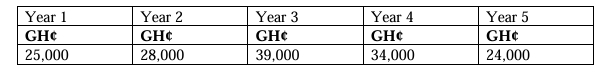
AK Plc is a company listed on the Nigerian Stock Exchange. It is involved in property development and sales.
The company currently imports more than 60% of its cement requirements. At a recent meeting of the board of directors, a decision was taken to establish a division for the production of cement in Ore, Ondo State. If the division is set up and the cement production goes ahead, output from the division will be sold to AK Plc and external customers at market price. For planning purposes, it has been decided that the financial viability of the project over the next five years should be determined.
The sum of N2 billion will be required. The sum of N500 million will be spent to acquire an existing factory considered suitable for the project. The balance of N1.5 billion will be applied for the procurement and installation of essential plant and equipment. Tax allowance can be claimed on plant and equipment at a uniform amount over 5 years with NIL scrap value.
A total of N20 million has been spent on various surveys (market, technical, financial, etc.) to date out of which N10 million has been paid. The balance of N10 million is due for payment at the end of year 1.
Production of cement for the next five years is projected as follows:
| Year |
Bags |
| 1 |
500,000 |
| 2 |
600,000 |
| 3 |
650,000 |
| 4 |
800,000 |
| 5 |
700,000 |
A bag of cement sells currently for N2,000 in the open market. This price is expected to increase at the rate of 5% per annum. Variable cost is now N1,000 per bag. This will increase at 4% per annum. Fixed overhead costs will be N50 million at current prices but will rise by 8% per annum. Apportioned head office charges of N25 million at current prices will rise by 10% per annum. Fifty per cent (50%) of the total initial outlay of N2 billion is to be funded with a loan from a Federal Government Development Bank at a concessionary fixed interest rate of 8%, payable at the end of each year. Half of the loan will be repaid at the end of year 3 while the balance will be paid at the end of year 5. The project will require a working capital of 10% of annual revenue, and this should be available at the beginning of each year.
The company uses a current Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) of 11% to appraise all capital projects. The asset beta of the company is 1.2, equity beta is 1.6, risk-free rate is 5%, while the market risk premium is 7%.
The Finance Director is of the view that it is not appropriate to use the existing WACC to appraise the new project. He has identified a listed company that currently produces cement and packaged fruit drinks. The company has the following financial statistics:
- Equity beta: 1.82
- Debt beta: 0.4
- Debt/Equity ratio: 40%
- 60% of the market value of the company is attributed to cement production, while 40% of the value is attributed to the fruit drinks division.
- The fruit drinks division has an equity beta of 0.8.
The new project is expected to move AK Plc to the target Debt/Equity ratio of 30%. Tax rate is 25% for the two companies and is paid in the year profit is made.
Required:
a. Compute the appropriate cost of capital that AK Plc should use to appraise the cement project and state why you consider this rate more appropriate than the existing WACC of 11%.
- Note: Your final cost of capital should be rounded up to the nearest whole number. State any assumptions made. (12 Marks)
b. Compute the Net Present Value (NPV) and Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) of the project, assuming a cost of capital of 13%.
- (Work to the nearest N million). (16 Marks)
c. Recommend whether the project should be accepted or not, using both NPV and MIRR methods. (2 Marks)