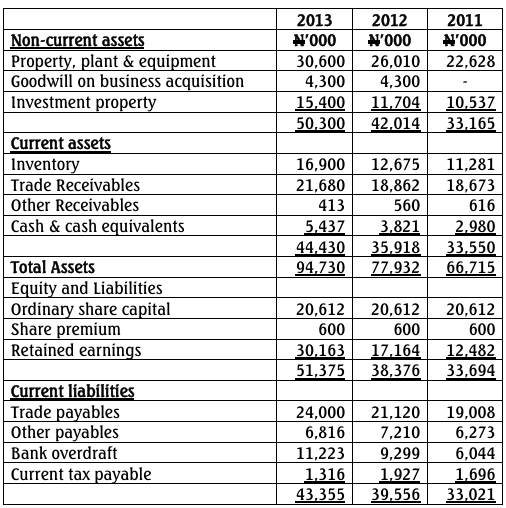
Neeta Ltd is a manufacturing company located in the Western Region. The trial balance of Neeta Ltd as at 31 March 2020 is as follows:
| Trial Balance |
GH¢’000 |
GH¢’000 |
| Revenue (Note i) |
|
164,000 |
| Production costs |
90,000 |
|
| Distribution costs |
8,000 |
|
| Administrative expenses |
26,000 |
|
| Inventory at 31 March 2019 |
19,710 |
|
| Interest paid on interest-bearing borrowings |
3,000 |
|
| Income tax (Note iii) |
100 |
|
| Dividends paid on equity shares |
5,000 |
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment (PPE) (Note iv) |
77,000 |
|
| Provision for depreciation on PPE at 31 March 2019 |
|
22,610 |
| Trade receivables |
53,000 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
33,000 |
|
| Trade payables |
|
12,000 |
| Long term interest-bearing borrowings |
|
50,000 |
| Lease rentals (Note v) |
20,000 |
|
| Deferred tax (Note iii) |
|
7,000 |
| Share capital |
|
50,000 |
| Retained earnings at 31 March 2019 |
|
29,000 |
| Totals |
334,710 |
334,710 |
Additional information:
i) On 1 April 2019, Neeta Ltd sold goods to a customer for a price of GH¢12.1 million. The terms of the sale allowed the customer extended credit, and the price was payable by the customer in cash on 31 March 2021. Neeta Ltd included the GH¢12.1 million in revenue for the current year and the corresponding entry in trade receivables. A discount rate that is appropriate for the risks in this transaction is 10%.
ii) The carrying value of inventory at 31 March 2020 was GH¢25 million.
iii) The estimated income tax on the profits for the year to 31 March 2020 is GH¢1.5 million. During the year, GH¢1.3 million was paid in full as the final settlement of income tax on the profits for the year ended 31 March 2019. The statement of financial position as at 31 March 2019 had included GH¢1.4 million in respect of this liability.
As at 31 March 2020, the carrying amounts of the net assets of Neeta Ltd exceeded their tax base by GH¢28 million. This information is before taking account of the Property revaluation (see Note iv below). The rate of income tax is 30%.
iv) Details of Property, Plant and Equipment are as follows:
| Component of PPE |
Cost (GH¢’000) |
Accumulated depreciation at 31 March 2019 (GH¢’000) |
Carrying Amount at 31 March 2019 (GH¢’000) |
| Land |
22,000 |
0 |
22,000 |
| Buildings |
28,000 |
5,600 |
22,400 |
| Plant and Equipment |
27,000 |
17,010 |
9,990 |
| Total |
77,000 |
22,610 |
54,390 |
The estimated useful economic life (at the date of purchase) of PPE components are:
- Land: Infinite life
- Building: 50 years
- Plant and Equipment: 4 years
On 1 April 2019, the property’s open market value was GH¢60 million, including GH¢32 million relating to the building. The directors wish to reflect this revaluation in the financial statements, but no entries regarding the revaluation have been made. The directors do not want to make an annual transfer of excess depreciation to retained earnings. The original estimate of the useful economic life of the building is still considered valid. No assets were fully depreciated at 31 March 2020. All the depreciation is to be charged to the cost of sales.
v) On 1 April 2019, Neeta Ltd leased a large group of machines used in the production process. The lease was for 4 years, and the annual rental (payable in advance) was GH¢20 million. The lessee has not elected to apply the recognition exemption under IFRS 16 leases. The interest rate implicit in the lease can be taken as 9% per year.
Required:
a) Prepare the Statement of Profit or Loss and Other Comprehensive Income for Neeta Ltd for the year ended 31 March 2020.
(10 marks)
b) Prepare the Statement of Financial Position for Neeta Ltd as at 31 March 2020.
(10 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)