- 14 Marks
ICMA – Nov 2024 – L1 – Q4a – Apportionment of Overheads
Apportion overhead costs across departments based on the most appropriate bases.
Question
: Apportionment of Overheads
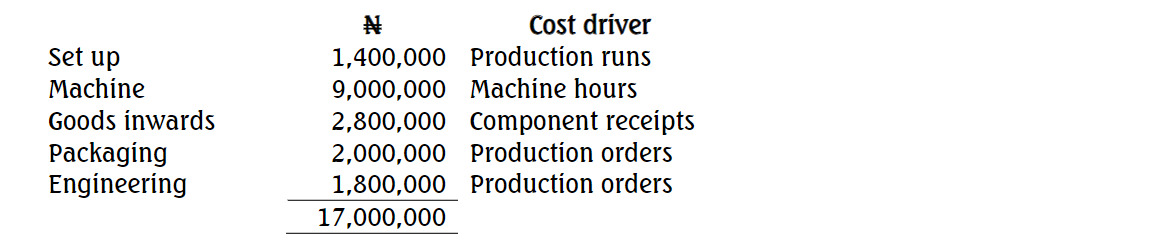
The following expenses were estimated for the month of June 2024:
| Item | GH¢ |
|---|---|
| Electricity | 80,000 |
| Rent | 18,000 |
| Property rate | 6,000 |
| Insurance premium (office equipment) | 15,000 |
| Internet and communication | 25,000 |
| Indirect wages | 60,000 |
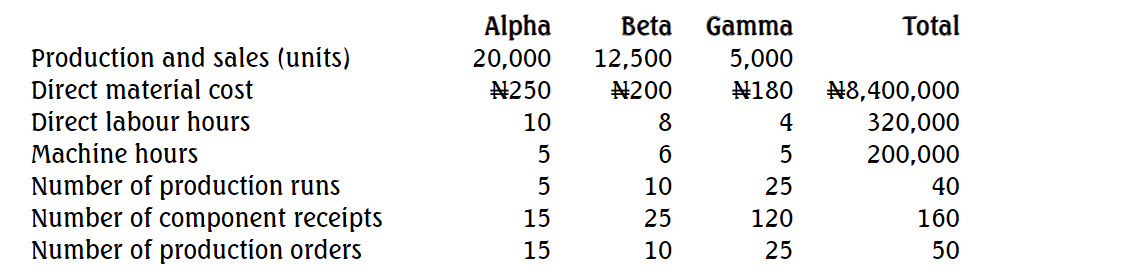
There are three departments: A, B, and C. The following additional information has been provided:
| Department | Area occupied (sq. metres) | Number of customers | Number of employees | Value of office equipment (GH¢) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 300 | 700 | 120 | 50,000 |
| B | 450 | 600 | 150 | 40,000 |
| C | 250 | 500 | 130 | 60,000 |
Required:
Apportion the above overheads using the most appropriate base and determine the total overhead for each department.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Cost Allocation, Departmental Costs, Overhead Apportionment
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Cost Segregation and Estimation
- Series: Nov 2024
Report an error