The recent trade tariff war on goods exported between the United States and China has opened a vista for corporate players in the two countries and their allies to venture into new areas considered to be business-friendly.
Sunchi Limited, Shanghai, is a computer accessories company that was incorporated in China in 2003. The company established its subsidiary outlet, Sunchi West Africa Holdings, in Ibadan, Nigeria, on January 1, 2018. The Nigerian company adopted December 31, annually (same as the parent company) as its end of financial year.
The first set of consolidated accounts was audited by a reputable audit firm based in China. Taxes for both business operations were also paid in China.
The Nigerian tax inspectors from the Federal Inland Revenue Service demanded for annual returns and tax computations from the subsidiary company but the General Manager of the company claimed that the company had paid personal income tax of its employees and directors, value-added tax on imported equipment, and relevant custom duties. Furthermore, since the parent company is not registered in Nigeria, there is no reason why it should be liable to companies’ income tax. The issue is yet to be resolved.
The Managing Director of the subsidiary company in Nigeria, with the permission of the head office in China, appointed you as the company‘s tax consultant to help unravel the issue of payment of companies’ income tax by resident and non-resident companies operating in Nigeria. He also submitted to you the statement of profit or loss for the year ended December 31, 2018, after conversion of the transactions in head office‘s Chinese currency (Yuan) to Nigerian Naira.
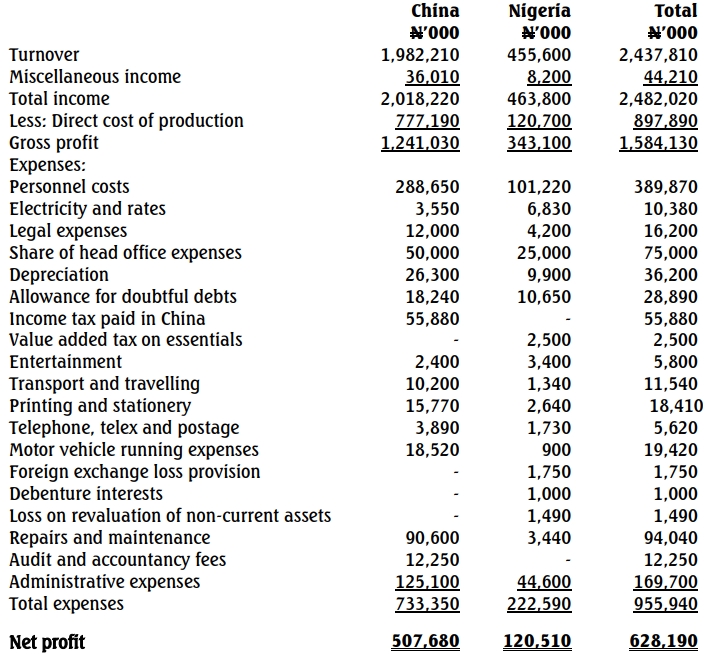
(i) Miscellaneous income:
This consists of income realised from the sale of component parts to the head office. The transaction was made at open market price.
(ii) Legal expenses comprise:
| Description |
Amount (N’000) |
| Debt collection |
800 |
| Preliminary expenses |
2,100 |
| Land acquisition |
550 |
| Retainership fee |
750 |
| Total |
4,200 |

Required:
As the company‘s tax consultant, you are to prepare a report to the management of Sunchi Limited taking into consideration the following:
a. Resident and non-resident companies (4 Marks)
b. Circumstances under which profit of a non-resident company will be liable to tax in Nigeria. (10 Marks)
c. Relationship between a:
- Nigeria branch and the parent company (3 Marks)
- Nigeria subsidiary and the parent company (3 Marks)
d. Overseas branch of a Nigerian company (3 Marks)
e. Overseas subsidiary of a Nigerian company (3 Marks)
f. Advise on, if any, the companies income tax payable by the two business operations in Nigeria. (14 Marks)