- 10 Marks
BCL – Nov 2024 – L1 – Q3b – Financial Assistance for Share Purchase
Conditions under which a company may provide financial assistance for share purchase.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Report an error
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
LL Plc. is a large engineering company. Its ordinary shares are quoted on the Stock Exchange.
LL Plc.’s Board is concerned that the company’s gearing level is too high and that this is having a detrimental impact on its market capitalisation. As a result, the Board is considering a restructuring of LL Plc.’s long-term funds, details of which are shown here as at 28 February, 2017:
| Funding Source | Total Par Value (₦m) | Market Value |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Share Capital (50k) | 67.5 | ₦2.65/share ex-div |
| 7% Preference Share Capital (₦1) | 60.0 | ₦1.44/share ex-div |
| 4% Redeemable Debentures (₦100) | 45.0 | 90% ex-int |
The debentures are redeemable in 2022. LL Plc.’s earnings for the year to 28 February, 2017 were ₦32.4 million and are expected to remain at this level for the foreseeable future. Retained earnings, as at 28 February, 2017 were ₦73.2 million.
The Board is considering a 1 for 9 rights issue of ordinary shares, and this additional funding would be used to redeem 60% of LL Plc.’s redeemable debentures at par. However, some of LL Plc.’s directors are concerned that this issue of extra ordinary shares will cause the company’s ordinary share price and its earnings per share (EPS) to fall by an excessive amount, to the detriment of LL Plc.’s shareholders. Accordingly, they are arguing that the rights issue should be designed so that the EPS is not diluted by more than 5%.
The Directors wish to assume that the income tax rate will be 21% for the foreseeable future and the tax will be payable in the same year as the cash flows to which it relates.
Required:
a. i. Calculate LL Plc.’s gearing ratio using both book and market values. (5 Marks)
ii. Discuss, with reference to relevant theories, why LL Plc.’s Board might have concerns over the level of gearing and its impact on LL Plc.’s market capitalisation. (6 Marks)
b. Assuming that a 1 for 9 rights issue goes ahead, calculate the theoretical ex-rights price of LL Plc.’s ordinary share and the value of a right. (3 Marks)
c. Discuss the Directors’ view that the rights issue will cause the share price and the EPS to fall by an excessive amount, to the detriment of LL Plc.’s ordinary shareholders. Your discussion should be supported by relevant calculations. (6 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
a. Past surveys revealed that one of the most important financial indicators in evaluating ordinary shares is the expected changes in earnings per share (EPS). Corporate earnings are a key component of these financial indicators, and, as far as investors are concerned, the quality of earnings is important in measuring a company’s prospects. The quality of earnings can be affected by several factors, which are at the discretion of management. A simple or complex capital structure also plays a vital role in the assessment of earnings quality and EPS.
Required:
i. What does “quality of earnings” connote, and how can it be assessed?
(5 Marks)
ii. What are the factors that can affect the quality of earnings of an organisation?
(3 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Yemi John Plc. (YJ) is planning to raise N30 million in new finance for a major expansion of its existing business and is considering a rights issue, a placing, or an issue of bonds. The corporate objectives of YJ, as stated in its annual report, are to maximize the wealth of its shareholders and to achieve continuous growth in earnings per share. Recent financial information on YJ is as follows:
| Year | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnover (Nm) | 28.0 | 24.0 | 19.1 | 16.8 |
| Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) (Nm) | 9.8 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 6.8 |
| Profit after tax (PAT) (Nm) | 5.5 | 4.7 | 4.1 | 3.6 |
| Dividends (Nm) | 2.2 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| Ordinary shares (Nm) | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Reserves (Nm) | 13.7 | 10.4 | 7.6 | 5.1 |
| 8% Bonds, redeemable 2024 (Nm) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Share price (N) | 8.64 | 5.74 | 3.35 | 2.67 |
The par value of the shares of YJ is N1.00 per share. The general level of inflation has averaged 4% per year in the period under consideration. The bonds of YJ are currently trading at their par value of N100. The values for the business sector of YJ are as follows:
EBIT/closing total capital employed
Required:
a. Evaluate the financial performance of YJ, analyzing and discussing the extent to which the company has achieved its stated objectives of:
i. maximizing the wealth of its shareholders; and
ii. achieving continuous growth in earnings per share. (13 Marks)
Note: Up to 8 marks are available for financial analysis.
b. Analyze and discuss the relative merits of a rights issue, a placing, and an issue of bonds as ways of raising finance for the expansion. (7 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
What will be the balance on the share premium account after the rights issue?
| Item | N’000 |
|---|---|
| Ordinary share capital: 200,000 shares of 50k each | 100 |
| Premium account | 150 |
The company made a rights issue of 1 for 5 at N1.50, and the rights issue was fully subscribed.
A. N90,000
B. N140,000
C. N150,000
D. N190,000
E. N200,000
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
The capital structure of Baba Oba Limited is shown below:
| Item | N’000 |
|---|---|
| Ordinary share capital: 200,000 shares of 50k each | 100 |
| Premium account | 150 |
The company made a rights issue of 1 for 5 at N1.50, and the rights issue was fully subscribed.
What is the amount of the rights issue credited to share capital?
A. N20,000
B. N40,000
C. N50,000
D. N70,000
E. N100,000
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
A firm has recently collected the following data in respect of its capital structure, expected earnings per share, and required rate of return.
| Debt Ratio % | Expected Earnings Per Share (N) | Required Rate of Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.10 | 14 |
| 10 | 3.80 | 16 |
| 20 | 4.60 | 17 |
| 30 | 5.25 | 19 |
| 40 | 5.70 | 20 |
| 50 | 5.00 | 22 |
| 60 | 4.50 | 24 |
You are required to:
a. Compute the estimated share values. (10 Marks)
b. Determine the optimal capital structure based on the maximization of expected earnings per share and the maximization of share values. (5 Marks)
c. Which capital structure criterion would you recommend and why? (5 Marks)
(Total: 20 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
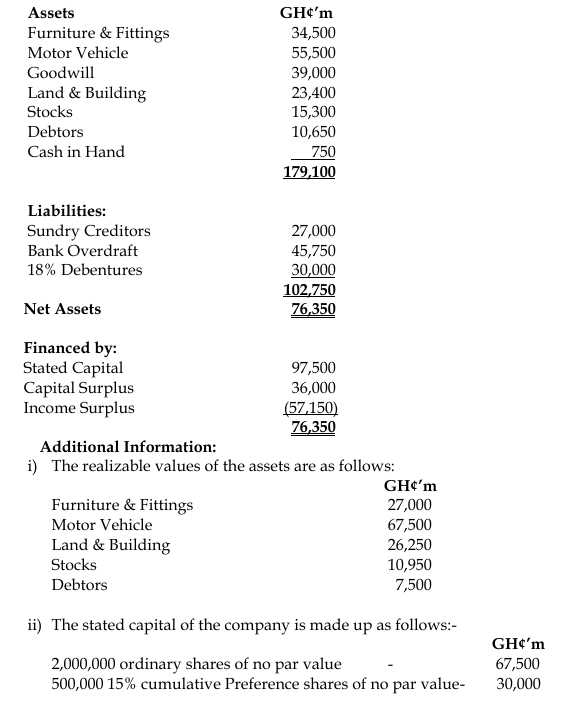
Additional Information:
Required:
a) Calculate the amount available if Crave Cottage Industry Limited is liquidated and its distribution.
(7 marks)
b) Calculate the maximum possible loss of Crave Cottage Industry Limited and its allocation to Preference Share Capital and Ordinary Share Capital. (6 marks)
c) Calculate the Bank/Cash balance of Crave Cottage Industry Limited after the reorganization. (2 marks)
d) Calculate the new stated capital for the company after the reorganization. (2 marks)
e) Prepare a Statement of Financial Position of Crave Cottage Industry Limited showing the position immediately after the scheme has been put in place.
(3 marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
c) Ten years ago, Brown Limited issued GH¢2.5 million of 6% discounted debentures at GH¢98 per 100 nominal. The debentures are redeemable in 5 years from now at GH¢2 premium over nominal value. They are currently quoted at GH¢80 per debenture ex-interest. Brown Limited pays corporate tax at the rate of 30%.
You are required to calculate the cost of debt after tax.
(4 marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Presented below are the common-sized financial statements of Towobo Ltd over the last five years:
Vertical Common-Sized Statements of Profit or Loss for the Years Ended 31 December
| % | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Cost of sales | (88.58) | (85.45) | (84.92) | (87.36) | (92.70) |
| Gross profit | 11.42 | 14.55 | 15.08 | 12.64 | 7.30 |
| Distribution & marketing costs | (1.00) | (0.86) | (0.83) | (1.15) | (0.87) |
| Administrative expenses | (0.74) | (0.79) | (0.88) | (0.85) | (0.73) |
| Other operating income | 2.06 | 1.78 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 0.69 |
| Other operating expenses | (1.36) | (0.86) | (1.21) | (1.20) | (0.94) |
| Profit from operations | 10.38 | 13.82 | 12.93 | 10.02 | 5.45 |
| Finance cost | (0.02) | (0.04) | (0.02) | (0.05) | (0.10) |
| Profit before tax | 10.36 | 13.78 | 12.92 | 9.97 | 5.35 |
| Tax | (3.25) | (3.98) | (4.05) | (3.25) | (2.61) |
| Profit after tax | 7.11 | 9.80 | 8.86 | 6.72 | 2.74 |
Vertical Common-Sized Statements of Financial Position as at 31 December
| % | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-current assets | |||||
| Property, plant & equipment | 8.49 | 8.55 | 15.50 | 20.27 | 23.33 |
| Intangible assets | 0.52 | 0.72 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.70 |
| Capital work-in-progress | 0.13 | 0.39 | 7.39 | 0.28 | 0.66 |
| Long-term loans & advances | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.52 | 3.20 | 3.65 |
| Total non-current assets | 9.47 | 9.88 | 23.85 | 24.26 | 28.31 |
| Current assets | |||||
| Inventories | 14.20 | 13.19 | 25.51 | 40.61 | 32.25 |
| Receivables | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.32 | – |
| Prepayments, advances, & other receivables | 22.33 | 17.65 | 6.21 | 10.69 | 20.33 |
| Short-term investments | 35.15 | 40.67 | 7.10 | – | – |
| Cash and bank balances | 18.69 | 18.52 | 36.80 | 24.12 | 19.11 |
| Total current assets | 90.53 | 90.12 | 76.15 | 75.74 | 71.69 |
| Total assets | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Equity | |||||
| Issued, subscribed & paid-up capital | 2.43 | 2.77 | 8.81 | 10.25 | 11.59 |
| Retained earnings | 16.50 | 10.69 | 18.24 | 3.78 | 0.62 |
| Other reserves | 10.10 | 11.91 | 21.95 | 22.74 | 7.20 |
| Total equity | 29.03 | 25.37 | 49.00 | 36.77 | 19.41 |
| Non-current liabilities | |||||
| Pensions liabilities | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.36 |
| Deferred tax | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.83 | – | – |
| Deferred revenue | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| Total non-current liabilities | 0.92 | 0.85 | 1.40 | 0.46 | 0.46 |
| Current liabilities | |||||
| Trade, dividend & other payables | 70.04 | 73.15 | 49.60 | 62.73 | 80.02 |
| Current portion of deferred revenue | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | – |
| Income tax | – | 0.62 | – | 0.01 | 0.11 |
| Total current liabilities | 70.05 | 73.78 | 49.60 | 62.77 | 80.13 |
| Total equity & liabilities | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Required:
As the Financial Advisor to ABC Mutual Funds, report on the financial health or otherwise of Towobo Ltd based on the vertically analysed financial statements and advise ABC Mutual Funds on whether to invest in Towobo Ltd. Your report should focus on the profitability and cost control analysis, asset structure, capital structure, and working capital structure.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Kinky Ltd is a manufacturing entity resident in Ghana. Mr. Andre Camil, a citizen and resident of France, owns 90% of the company’s shares. Mrs. Claude Camil, a citizen and resident of France and wife of Mr. Andre Camil, also owns 5% of the shares of the company. Mr. Francois Camil, the son of Mr. Andre Camil, holds the remaining 5% of the shares in the company.
As at 1 June, 2021, the company had a share capital of GH¢400,000. A report submitted by the management to the Board of Directors indicated that the company needs to acquire a plant valued at GH¢1,000,000 to enable the company to increase its production capacity. Mr. Andre Camil, the majority shareholder, has offered to finance the purchase of the plant for the company but his challenge is whether to provide the asset to the company as a loan or as equity.
Required:
Advise Mr. Andre Camil on:
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
On 1 January 2022, Frost Ltd based in the United States of America acquired 100% shares in Nzungu Ltd in the Gambia. Also, Nzungu Ltd acquired 60% shares in Gyakye Ltd in Ghana.
Frost Ltd granted a loan equivalent of GH¢100 million to Nzungu Ltd. The loan was subsequently passed on to Gyakye Ltd in Ghana to strengthen its capital structure.
The interest equivalent on the loan from Frost Ltd to Nzungu Ltd was GH¢6,000,000. Gyakye Ltd ended up paying GH¢8,000,000 as interest to Nzungu Ltd. The difference in interest payment was a service charge for the role played in transferring the loan to Ghana by Nzunga.
Gyakye Ltd has the following extracts from its Statement of Financial Position as at 2022:
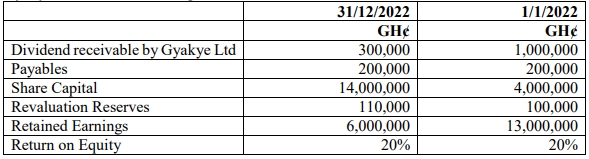
Required:
Evaluate the tax implications of the following:
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Firm A and Firm B are both subsidiary companies of Groupe Trojan Electronics. The directors of Groupe Trojan Electronics are reviewing the capital structure of the two subsidiary companies. You have been engaged to advise the directors on the appropriate capital structure for the subsidiaries.
You have obtained extracts from the financial results of the two companies for the past financial year and projection of the annual results for the current year, which is in its first quarter.
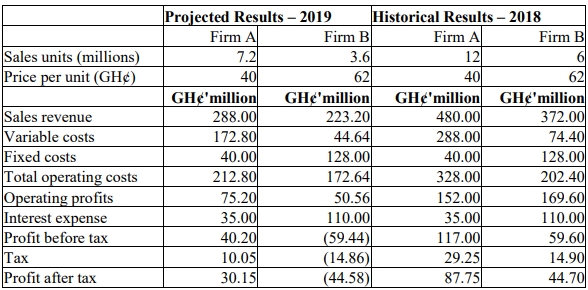
Required:
i) Compute the degree of operating leverage for each of the two companies. Based on the degree of operating leverage you obtain, advise the directors on the relative level of business risk associated with the two subsidiaries and the implication of that for capital structure design. (5 marks)
ii) Compute the degree of financial leverage for each of the two companies. Based on the degree of financial leverage you obtain, advise the directors on the relative level of financial risk associated with the two subsidiaries and the implication of that for capital structure design. (5 marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
a) The Directors of Moore Plastics Ltd have been deliberating on the company’s capital structure with a view to identifying an optimal financing mix. Opening the deliberation, the Board Chair remarked, “For the past 10 years, we have deployed a financing strategy of reinvesting as much profit as available. When profit is inadequate, we go for borrowing. New equity offers have been a last resort.”
Required:
i) Explain with THREE reasons why most managers tend to use financing strategies that follow the pecking order. (6 marks)
ii) Identify and explain TWO factors the directors of Moore Plastics Ltd should consider in redesigning the company’s capital structure. (4 marks)
b) Pusher Mining Ltd, a large listed company, operates five mineral concessions in Ghana and Ivory Coast. The company’s financial performance for the past five years has been impressive. The company’s recently published financial results indicate that it earned after-tax profit of GH¢250 million and paid dividends of GH¢50 million out of that profit.
Reserves at two of the five mineral concessions will be exhausted in two years’ time, and stakeholders fear this will adversely affect the company’s profitability. Nevertheless, the directors are aiming at maintaining the company’s dividend payment record. To achieve this, they want to pursue a new project in the oil industry to provide additional cash flows. Though the new project will be financed with existing equity and long-term debts, the directors are not sure what cost of capital to use in appraising the new project.
A summary of the company’s financial position before the new oil project follows:
| Item | GH¢m |
|---|---|
| Noncurrent assets | 620 |
| Current assets | 425 |
| Total assets | 1,045 |
| Equity | |
| Stated capital | 180 |
| Income surplus | 685 |
| Shareholders’ fund | 865 |
| Liabilities | |
| Current liabilities | 20 |
| Bank loans | 40 |
| Bonds | 120 |
| Total liabilities | 180 |
| Total equity and liabilities | 1,045 |
Notes:
If the new oil project is implemented, Pusher Mining Ltd’s main competitor in the oil industry would be Cargo Oil Ltd. The estimated equity beta of the competitor is 1.80 and the market value of its equity stock is GH¢150 million. The long-term debt stock of the competitor is valued at GH¢100 million. The systematic risk of debt stocks is assumed to be zero. The risk-free return is 14% and the market return is 20%. The corporate tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Estimate the appropriate cost of capital Pusher Mining Ltd should use in appraising the new project in the oil industry. Show all relevant computations. (10 marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Boom Ltd is into the provision of online conference call facilities which has become popular due to the rising trend in Covid-19 cases in Ghana. The company has 10 million issued shares currently at GH¢50 each, 3 million preference shares trading at GH¢25 each, and 5,000 bonds also trading at GH¢600 each.
Required:
i) Calculate the Capital Structure of the Company. (4 marks)
ii) How much should the company earn annually to achieve a return of 25% per annum on capital employed for equity holders if the dividend rate on preference shares per annum is 20% and the coupon on the bonds is 18%? In Ghana, interest paid on debt is tax deductible and corporate tax is at 25%. (6 marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
If an existing public company chooses to issue shares, the financial market usually interprets this as a sign that the company’s share price is somewhat overvalued. To avoid this negative impression, a company may choose to issue convertible bonds, which bondholders are likely to convert to equity anyway should the company continue to do well.
Required:
Explain convertible debt and identify FOUR (4) attractions to a company of convertible debt compared to a bank loan of a similar maturity as a source of finance. (5 marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.

Elevate your professional expertise across key business domains with our comprehensive training programs
Follow us on our social media and get daily updates.
This feature is only available in selected plans.
Click on the login button below to login if you’re already subscribed to a plan or click on the upgrade button below to upgrade your current plan.
If you’re not subscribed to a plan, click on the button below to choose a plan