- 15 Marks
Question
YSL is a company located in the USA that has a contract to purchase goods from Japan in two months’ time on 1st September. The payment is to be made in yen and will total 140 million yen. The managing director of YSL wishes to protect the contract against adverse movements in foreign exchange rates and is considering the use of currency futures. The following data are available:
- Spot foreign exchange rate: $1 = 128.15 yen
- Yen currency futures contracts on SIMEX (Singapore Monetary Exchange)
- Contract size: 12,500,000 yen
- Contract prices (US$ per yen):
- September: 0.007985
- December: 0.008250
Assume that futures contracts mature at the end of the month.
Required:
i) Illustrate how YSL might hedge its foreign exchange risk using currency futures. (5 marks)
ii) Explain the meaning of basis risk and show what basis risk is involved in the proposed hedge. (5 marks)
iii) Assuming the spot exchange rate is 120 yen/$1 on 1 September and that basis risk decreases steadily in a linear manner, calculate what the result of the hedge is expected to be. Briefly discuss why this result might not occur. (5 marks)
(Margin requirements and taxation may be ignored.)
Answer
(a) (i)
YSL can hedge using futures as follows.
• Use September futures, since these expire soon after 1 September, price of 1/0.007985
= 125.23 ¥/$.
• Buy futures, since it wishes to acquire yen to pay the supplier, and the futures are in
Yen.
• Number of contracts 140m/12.5m = 11.2 contracts – 11 contracts
• Tick size
0.000001 x 12.5m = $12.50
ii) Explanation of basis risk and basis risk in the proposed hedge:
Basis risk arises when the price of a futures contract does not move in perfect correlation with the value of the underlying asset being hedged. In YSL’s case, the price of the yen currency futures might not track the spot exchange rate exactly, leading to potential profit or loss from the difference.
Basis risk in this case:
- Spot price = 1 / 128.15 = 0.007803
- Basis = Spot price – Futures price
= 0.007803 – 0.007985 = -0.000182 (182 ticks)
With 3 months to expiry, basis is 182 ticks. If the basis decreases uniformly, with one month to expiry, basis would be:
Basis = 182 ticks × (1/3) = 61 ticks.
Spot price on 1 Sept = 1/120 = 0.008333
Therefore predicted futures price = 0.008333+0.000061= 0.008394
(5 marks)
iii) OutcomeFutures market
Opening futures price 0.007985
Closing futures price 0.008394
Movement in ticks 409 ticks
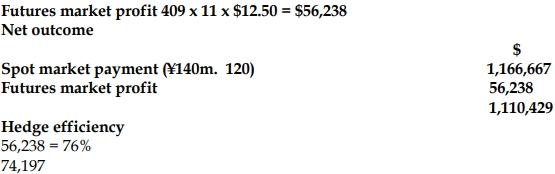
This hedge is not perfect because there is not an exact match between the exposure and
the number of contracts, and because the spot price has moved more than the futures
price due to the reduction in basis. The actual outcome is likely to differ since basis risk
does not decline uniformly in the real world.
- Tags: Basis risk, Currency Futures, Currency Hedging, Foreign Exchange Risk, Risk Management
- Level: Level 3
- Uploader: Kwame Aikins
