- 15 Marks
Question
Obong plc recently received a takeover bid from Abdul plc. If the bid for Obong plc is successful, it will provide Abdul plc the needed competitive edge in research and development to expand its laboratories into the production of the COVID-19 vaccine.
The shareholders of Obong plc will only accept an offer that meets a required return of 14% on their current shareholdings.
Obong plc recently paid a dividend of N20, and this is expected to grow at a rate of 7% for the foreseeable future.
Required:
a. Estimate the share price of Obong plc today. (2 Marks)
b. If Obong plc accepts the bid from Abdul plc, it is estimated that the new growth rate will rise to 12% for the first 3 years and thereafter stabilize at 7%. Calculate the new share price to the shareholders of Obong plc. (2 Marks)
c. As a financial advisor, recommend to the shareholders of Obong plc whether the offer from Abdul plc should be accepted. (2 Marks)
d. According to Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH), it is believed that the market would react instantly and accurately to the merger announcement between Obong plc and Abdul plc.
Define briefly the THREE forms of EMH and their implications to the market. (9 Marks)
Answer
a) Current share price:
P0 = D1/(r − g)
= 20(1.07)/(0.14 – 0.07)
= ₦305.71
b) Revised share price
PV of future dividends:
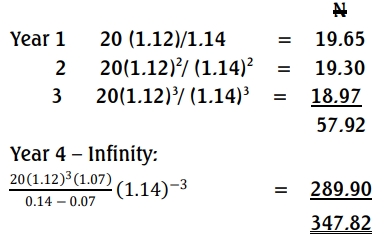
c) The offer for takeover is expected to increase the share price from ₦305.71 to ₦347.82 and if all other factors remain constant, the offer should be accepted.
d) The Three Forms of Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) and Their Implications:
- Weak-Form EMH:
- Definition:
The weak-form EMH asserts that current stock prices fully reflect all historical market information, such as past prices, rates of return, and trading volumes. - Implications:
- Past market data, including historical rates of return, has no predictive value for future rates of return.
- Investors cannot consistently earn excess returns using technical analysis or trading rules based on historical data.
- Market prices are considered to follow a random walk, making technical analysis ineffective.
- Definition:
- Semi-Strong Form EMH:
- Definition:
The semi-strong form EMH states that current market prices reflect all publicly available information, including historical market data and non-market public information, such as earnings reports, dividend announcements, stock splits, and economic or political news. - Implications:
- Investors cannot consistently achieve above-average returns using publicly available information, as it is already incorporated into the stock price.
- Fundamental analysis, such as calculating the intrinsic value of shares, becomes unproductive in identifying mispriced securities in an efficient market.
- This form assumes that markets adjust rapidly and accurately to new public information.
- Definition:
- Strong-Form EMH:
- Definition:
The strong-form EMH contends that stock prices fully reflect all information, both public and private. This implies that no group of investors has monopolistic access to any information relevant to stock prices. - Implications:
- Even insiders with access to private information cannot consistently achieve above-average risk-adjusted returns.
- Markets are assumed to be “perfect,” where all information is freely and simultaneously available to all market participants.
- The strong form incorporates the assumptions of the weak-form and semi-strong form EMH but extends it to include private information.
- Definition:
- Topic: Mergers and acquisitions
- Uploader: Kofi
