- 20 Marks
Question
- Yinko plc operates in the hospitality and leisure industry. The board of directors met recently to discuss several financial proposals:
- Proposal 1: Increase the company’s debt by borrowing an additional N100 million and use the funds raised to buy back its shares.
- Proposal 2: Increase the company’s debt by borrowing an additional N100 million to invest in expanding available rooms in one of its hotels.
- Proposal 3: Sell excess non-current assets in another hotel with a net book value of ₦100 million for N135 million. The funds from the sale will be used to reduce the company’s debt.
Yinko plc Financial Information:
Amount (N Million) Non-current assets 1,410 Current assets 330 Total assets 1,740 Equity and liabilities Share capital (40 kobo per share par value) 240 Retained earnings 615 Total equity 855 Non-current liabilities 700 Current liabilities 185 Total liabilities 885 Total liabilities and capital 1,740 Additional Information:
- Yinko’s forecasted after-tax profit for the coming year, without implementing the proposals, is N130 million.
- Current share price: N3.20 per share.
- Non-current liabilities include a 6% medium-term loan redeemable in seven years. Any increase in borrowing raises the coupon rate by 25 basis points on the total amount borrowed, while a reduction lowers it by 15 basis points.
- Effective tax rate: 20%
- Expected after-tax return on investment: 15% for new or reduced investments.
Required:
a. Estimate the impact of each proposal on the forecast statement of financial position, earnings per share, and financial gearing (Total Debt/Total Assets) of Yinko Plc. Show all calculations. (16 Marks)
b. Discuss your results. (4 Marks)
Answer
a) Forecast Financial Position – Yinko Plc
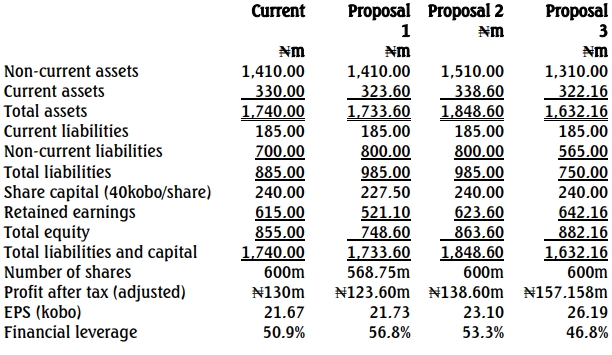
Working Notes
Proposal 1
Debt is increased by ₦100million and shareholders fund reduced by the same amount as follows:
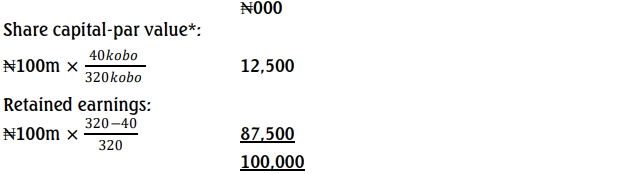
(* Only the par value can be removed from share capital. This is very important please)

This is taken from retained earnings.
Balance of retained earnings
= ₦615m – (87.50m + 6.40m) = ₦521.10m
Furthermore, the additional interest of ₦6.40m is taken off current assets because presumably it is paid out of cash.
Balance of current assets = 330m – 6.40m = ₦323.60m
The alternative is to assume that the additional interest has not been paid and therefore taken to interest payable in current liabilities. That leaves current assets constant at ₦330m and increases current liabilities to ₦191.40m.
Adjusted PAT = ₦130m – 6.40m = ₦123.60m
Proposal 2
Borrowing of ₦100m increases non-current assets and non-current liabilities
by the same amount.
Retained earnings and current assets are impacted as follows

Proposal 3
Non-current assets are reduced by ₦100m (the net book value of the assets sold). The profit on disposal of ₦100m increases retained earnings (through profit and loss account). The net change in retained earnings and current assets are as follows:


b. Proposal 1 appears to produce opposite results compared to the other proposals. This proposal would lead to a small increase in the earnings per share (EPS) due to a reduction in the number of shares. However, the level of gearing would reduce substantially, by about 12%.
With Proposal 3, overall profits would increase because the profit from the sale of assets combined with interest savings outweighs the lost earnings from downsizing. This proposal also results in the lowest gearing level.
Proposal 2 would significantly boost the EPS from 21.67 kobo to 23.10 kobo, primarily due to increased earnings through extra investment. However, the amount of gearing would increase by more than 4.7%.
Overall, Proposal 1 appears to be the least attractive option. The choice between Proposals 2 and 3 would depend on the sustainability of earnings versus reduced gearing. Proposal 3 may not be sustainable because the profit from asset sales is a one-off transaction.
Other factors to consider include the capital structure of competitors, the reaction of the equity market to the proposal, the implications of the change in the company’s risk profile, and the resultant impact on the cost of capital.
- Tags: Asset sale, debt level, EPS, Financial Gearing, Financial restructuring, Non-current Assets, share buyback
- Level: Level 3
- Uploader: Kofi
